Superseding Visa’s Payment Application Best Practices (PABP), The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a global set of security best practices which, when implemented correctly, will assist adhering parties in protecting their systems and help maintain the trust of their customers and clients.
There are three security standards managed by the PCI SSC:
1. The PCI PTS is the security standard that ensures hardware devices are manufactured to secure specifications and reduces the risk of tampering/misuse; devices are built with secure hardware encryption.
2. The software/firmware loaded onto the hardware must be PA-DSS compliant. The instructions sent from the software must adhere requirements outlined in the standard, encrypting data to a sufficient algorithm before transmitting the transactional data.
3. The PCI DSS is the security standard for the Cardholder Data Environment it is necessary for all entities that handle payment card/account data (cardholder and sensitive authentication data) – which is the one relevant to you.
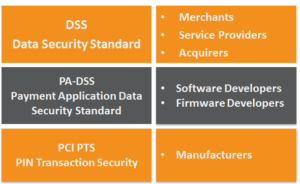
The PCI DSS is one size fits all and not industry-specific, therefore some requirements may prove more challenging for certain organizations such as handling payment card processing within a call centre for utilities, etc. versus the requirements for online retail merchants.
The PCI DSS undergoes on-going amendments and appendages, with a new version released every three years. This is to ensure that the standards maintained and current with technological advances, security breaches, and policy shifts.
The maintenance of the standard is the responsibility of the PCI Security Standards Council. The PCI SSC was founded and is executively run by the five major global card schemes: Visa Inc. (& Europe); American Express; Discover Financial Services; MasterCard and JCB International. It was founded in 2006, is an open, international forum and hold annual conferences.
To ensure sufficient feedback is provided on upcoming amendments and appendages to the PCI standards, many of the worlds larger, international corporations are represented on the PCI SSC’s Board of Advisors. The board has representatives from the different industries involved in the Payment Card Industry including coffeehouse chain Starbucks, U.S retailer Walmart, network hardware manufacturer Cisco along with Acquirers Barclaycard and HSBC Global Payments.
PCI is enforced by card schemes via your acquirer. You will need to be annually accredited. PCI adherence and the related fines are part of the MSA agreement, so you have no option but to be PCI compliant. It applies to any entity that handles payment card /account data (cardholder and sensitive authentication data); i.e. the merchant, your gateway and acquirer.
Fines
Deloitte Analysis on Card Scheme Fines: Taking a quite modest compromise of 10,000 cards at a merchant, you could expect to have compromise fees of 5 pounds per card; investigation costs of about £30,000; an average fraud of £1,000 euros per card, card replacement costs of £20 per card; and £30 per card in chargeback fees. That comes to over £10,000,000.
1. Fines occur when merchants, service providers, and acquirers are found to be non-compliant. This is referred to as an Account Data Compromise (ADC).
2. The Card Schemes are entitled to issue fines to acquirers whose merchants are found non-compliant and have had a security breach. It is the responsibility of the acquirer to pass on these fines (with forensic investigation and remediation costs: card replacements & chargeback fees) onto the merchant. The average fine issued by Barclaycard is around £15,000. All these fees and fines are exclusive of the overall loss of revenue and inventory…
3. It is important to note, however, that on top of non-compliance fines that may be levied at any time by the Card Schemes when the non-compliance deadline has passed, compromise fines will be levied in all cases where merchants are found to be non-compliant and the subject of a security breach.
4. 40% of Merchants are non-compliant.
Cardholder Data Environment
The cardholder data environment consists of the people, processes, technologies and the transmission of cardholder data or sensitive authentication data.
People – The PCI DSS Standard requires that background checks (police/ credit/ reference) are performed on new employees. This is to mitigate the risk of internal attacks on the credit card environment and to ensure credentials are not provided to would-be fraudsters.
In addition, it is a compliance requirement that all staff handling payment card
processing/account data are educated on information security and are made aware of risks, and are able to proactively identify possible fraudulent transactions.
Processes – The methodologies used when capturing and processing cardholder data. This would include not writing down credit card numbers, ensuring staff have a unique identification. Vulnerability management programs must be created and Infrastructure staff working on the on processing interfaces should monitor and test the network for vulnerabilities. In the scenario of a security breach, structures must be in place to ensure that the loss of data is limited.
Technologies – An example of PCI Compliant technologies would be the Realex Virtual Terminal. A secure platform where merchants can take MOTO (Mail Order/ Telephone Order) transactions on a secure, compliant platform. Applications & hardware used to process transactions must be compliant with the security processes outlined in the PCI DSS
Transmission – Whilst data entry and on-site encryption may be compliant, if the data is sent via an insecure network/protocol, the exposed information would be at risk to attack. Therefore PCI DSS requires that all financial data sent/ received within the cardholder data environment is to the latest recognized standards.
Cardholder Data

Cardholder Data is the information on the payment card excluding any data that would authenticate the cardholder i.e. “digital signature”. This is the information that is “embossed” and would be recorded by a card imprint device/ ZipZap machine.
PCI DSS permits the storage of the cardholder data providing compliance requirements are met. When stored on a database, the Card Number must be encrypted upon capture and not returned to plaintext. To identify cards securely, the first six (BIN) and last four may be displayed:
xxxx xx00 0000 0000 – BIN Bank Identification Number
The BIN is used to identify the bank who issued the card. This value is important for determining the card issuer and their geographical location. An important part of fraud prevention, this would allow merchants to restrict credit card holders from outside the merchant’s country from processing on their website.
0000 0000 0000 000x – Luhn Check Digit
To reduce the incorrect entry of credit card numbers in systems where validation may not occur, PANs are subject to the Luhn check algorithm. A mathematical equation which verifies the sum of its figures against the final value/digit of the card number. Information on how the Luhn check algorithm determines this number can be found here:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luhn_algorithm.
Sensitive Cardholder Data

Sensitive Authentication Data relates to the ‘digital signature’ of the Credit Card. These are the values used to identify that the card has been processed by the cardholder.
It cannot be recorded for any purpose, including recurring billing, tokenization, etc.
For the Card Not Present environment this would be the 3D Secure Password and the four-digit CID(AmEx), or three-digit CAV2/CVC2/CVV2.
Storing the CVV would result in PCI Compliance breach and the guilty party would be subject to fines.
Compliance
The PCI DSS is built on 12 requirements; these are surmised to six key modules:
Build and Maintain a Secure Network
Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data and do not use vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters.
Protect Cardholder Data
Protect stored cardholder data and encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks. A Payment Processor also offers a tokenisation service, which means you would only need to store tokens. We are happy to advise you on how to implement this service.
Maintain a Vulnerability Management Program
Protect all systems against malware and regularly update anti-virus software or programs and develop and maintain secure systems and applications.
Implement Strong Access Control Measures (User Credentials & Biometrics)
Restrict access to cardholder data by business need to know, identify and authenticate access to system components and restrict physical access to cardholder data.
Regularly Monitor and Test Networks
Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data and regularly test security systems and processes.
Maintain an Information Security Policy
Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel.
Gaining Compliance

PCI Compliance functions on a tiered structure of three levels with level one being the highest level of compliance. Each Card Scheme has slightly different determinations of what criteria determine the Merchant/Service Providers level requirements. The criteria are generally based on annual transaction volumes. This slide presentation is an example of Visa’s merchant tier structure. (source: http://www.visaeurope.com/en/businesses__retailers/payment_security/merchants.aspx)
Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ)
The PCI DSS SAQ is a validation tool for merchants and service providers that are not required to undergo an on-site data security assessment per the PCI DSS Security Assessment Procedures. The purpose of the SAQ is to assist organizations in self-evaluating compliance with the PCI DSS, and you may be required to share it with your acquiring bank. Please consult your acquirer for details regarding your particular PCI DSS validation requirements.
On-Site Visits: Qualified Security Assessor (QSA)
QSAs are PCI approved companies and professionals who can assess merchant/service providers’ compliance with PCI DSS. Approved Scanning Vendor(ASV) validate PCI Compliance by performing vulnerability scans of internet-facing environments of merchants and service providers. In addition to QSAs, The PCI SSC Internal Security Assessor (ISA) Program provides large merchants, acquiring banks, and processors the opportunity to build their internal PCI Security Standards expertise and strengthen their approach to payment data security, as well as increase their efficiency in compliance with the PCI Data Security Standards.
Quarterly Network Scans: Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV)
Approved Scanning Vendors (ASVs) are organizations that validate adherence to certain DSS requirements by performing vulnerability scans of Internet-facing environments of merchants and service providers. The Council has approved more than 130 ASVs.

